- Tree is a hierarchical data structure which stores the information naturally in the form of hierarchy style.
- Tree is one of the most powerful and advanced data structures.
- It is a non-linear data structure compared to arrays, linked lists, stack and queue.
- It represents the nodes connected by edges.
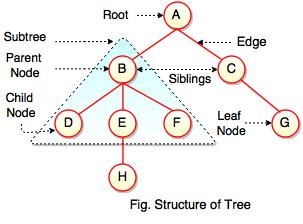
The above figure represents structure of a tree. Tree has 2 subtrees.
A is a parent of B and C.
B is called a child of A and also parent of D, E, F.
Tree is a collection of elements called Nodes, where each node can have arbitrary number of children.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Root | Root is a special node in a tree. The entire tree is referenced through it. It does not have a parent. |
| Parent Node | Parent node is an immediate predecessor of a node. |
| Child Node | All immediate successors of a node are its children. |
| Siblings | Nodes with the same parent are called Siblings. |
| Path | Path is a number of successive edges from source node to destination node. |
| Height of Node | Height of a node represents the number of edges on the longest path between that node and a leaf. |
| Height of Tree | Height of tree represents the height of its root node. |
| Depth of Node | Depth of a node represents the number of edges from the tree's root node to the node. |
| Degree of Node | Degree of a node represents a number of children of a node. |
| Edge | Edge is a connection between one node to another. It is a line between two nodes or a node and a leaf. |
In the above figure, D, F, H, G are leaves. B and C are siblings. Each node excluding a root is connected by a direct edge from exactly one other node
parent → children.
Levels of a node
Levels of a node represents the number of connections between the node and the root. It represents generation of a node. If the root node is at level 0, its next node is at level 1, its grand child is at level 2 and so on. Levels of a node can be shown as follows: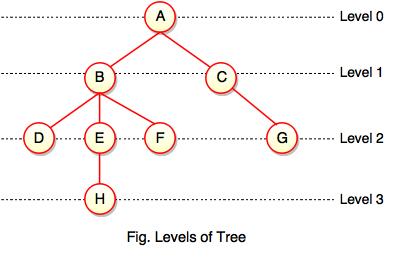
Note:
- If node has no children, it is called Leaves or External Nodes.
- Nodes which are not leaves, are called Internal Nodes. Internal nodes have at least one child.
Height of a Node
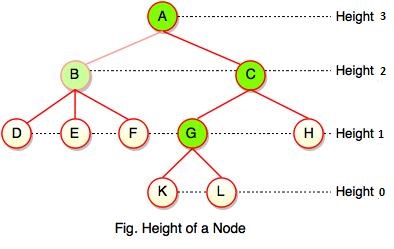
As we studied, height of a node is a number of edges on the longest path between that node and a leaf. Each node has height.
In the above figure, A, B, C, D can have height. Leaf cannot have height as there will be no path starting from a leaf. Node A's height is the number of edges of the path to K not to D. And its height is 3.
Note:
- Height of a node defines the longest path from the node to a leaf.
- Path can only be downward.
Depth of a Node
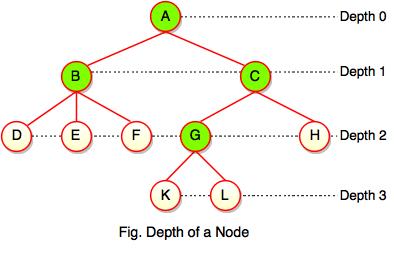
While talking about the height, it locates a node at bottom where for depth, it is located at top which is root level and therefore we call it depth of a node.
In the above figure, Node G's depth is 2. In depth of a node, we just count how many edges between the targeting node & the root and ignoring the directions.
Note: Depth of the root is 0.
Advantages of Tree
- Tree reflects structural relationships in the data.
- It is used to represent hierarchies.
- It provides an efficient insertion and searching operations.
- Trees are flexible. It allows to move subtrees around with minimum effort
No comments:
Post a Comment